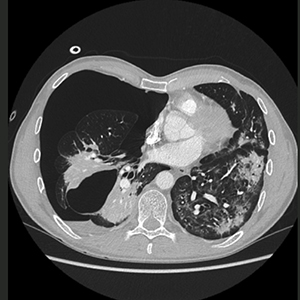
Full medical treatment of COVID-19 associated large pneumothorax - A case report
Published: September 28, 2021
Abstract Views: 917
PDF: 433
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Similar Articles
- Evaggelina Papakanderaki, Konstantinos Kanakakis, Sotirios Goule, Maria Chounti, Panagiotis Hountis, Clinical significance of positive Raoultella Ornithinolytica and Staphylococcus hominis cultures in a post lobectomy patient. A case report , Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease: Vol. 88 No. 1 (2018)
- X. Dhalluin, A. Scherpereel, Treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: current status and future directions , Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease: Vol. 73 No. 2 (2010): Pulmonary series
- B.D. Grigoriu, C. Grigoriu, B. Chahine, T. Gey, A. Scherpereel, Clinical utility of diagnostic markers for malignant pleural mesothelioma , Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease: Vol. 71 No. 1 (2009): Pulmonary series
- Rahul Tyagi, Saurabh Mittal, Karan Madan, Anant Mohan, Vijay Hadda, Pawan Tiwari, Randeep Guleria, Assessment of the impact and reorganization of interventional pulmonology services at a tertiary care centre during nationwide lockdown for COVID-19 pandemic , Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease: Vol. 91 No. 1 (2021)
- Michele Vitacca, Piero Ceriana, Bruno Balbi , Claudio Bruschi, Maria Aliani, Mauro Maniscalco, Francesco Fanfulla, Aldo Diasparra, Luigino Rizzello, Daniela Sereni, Antonio Spanevello, The respiratory rehabilitation Maugeri network service reconfiguration after 1 year of COVID-19 , Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease: Vol. 91 No. 4 (2021)
- Manas Pratim Roy, Risk factors for Covid-19 in India , Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease: Vol. 92 No. 2 (2022)
- Grigoris Stratakos, Vlassis Vitsas, Nikos Koufos, Charalambos Zissis, Philip Emmanouil, Nikos Koulouris, Post-pneumonectomy and post-lobectomy syndromes: case series and review of the literature , Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease: Vol. 87 No. 1 (2017)
- N. Facciolongo, R. Piro, F. Menzella, M. Lusuardi, M. Salio, L. Lazzari Agli, M. Patelli, Training and practice in bronchoscopy. A national survey in Italy , Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease: Vol. 79 No. 3-4 (2013): Pulmonary series
- Grazia Mazzeo, Luigi Aronne, Domenica Francesca Mariniello, Valentino Allocca, Maria Ilaria Palma, Francesco Saverio Cerqua, Carlo Iadevaia, Adriano Costigliola, Roberto Parrella, Andrea Bianco, Vanvitelli/Monaldi COVID Group, Which impact for proton pump inhibitors in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia , Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease: Vol. 91 No. 4 (2021)
- Carlo Iadevaia, Fabio Perrotta, Grazia Mazzeo, Francesco Saverio Cerqua, Gennaro Mazzarella, Salvatore Guarino, Roberto Parrella, Andrea Bianco, Incidental diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma following coronavirus OC 43 severe pneumonia , Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease: Vol. 90 No. 3 (2020)
<< < 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 > >>
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/monaldi.2021.1956
https://doi.org/10.4081/monaldi.2021.1956





