Coronavirus disease 2019 and mechanical circulatory support devices: a comprehensive review
Accepted: August 30, 2022
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
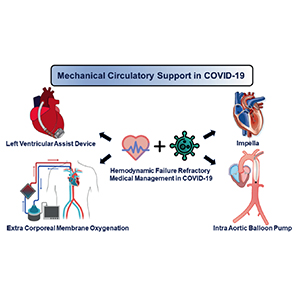
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) can cause circulatory shock refractory to medical therapy. Such patients can be managed with mechanical circulatory support (MCS) devices like IABP, Impella, VA ECMO, and Left Ventricular Assist Devices (LVADs). Moreover, patients on long-term durable LVADs are a special population having increased susceptibility and mortality to COVID-19 infection. In this narrative review, we searched PubMed and Medline for studies on COVID-19 patients on short-term MCS devices. We found 36 papers with 110 patients who met our review criteria, including 89 LVAD patients and 21 COVID-19 patients who needed MCS device therapy. These studies were used to extract patient demographics, clinical presentation, MCS device details, management, and outcomes. Mean age of patients with COVID-19 infection on LVADs was 60, 73% were male, and HeartMate 3 was the most common device (53%). Most patients (77.5%) needed hospitalization, and mortality was 23.6%. Among the 21 reported cases of critically ill COVID-19 patients who required MCS, the mean age was 49.8 years, 52% were women, and the most common MCS device used was VA ECMO (62%) in conjunction with an Impella for LV venting. Comorbidities were not present in 43%, but 71% had abnormal ventricular function on echocardiography. MCS is a viable option for managing severe COVID-19 infection with shock, with many reported cases of favorable outcomes.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.
Similar Articles
- Mohammad Samet, Hossein Soleimani Salehabadi, Pulmonary infection with an unusual microorganism , Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease: Early Access
- Paola Pierucci, Lucrezia De Michele, Maria Luisa de Candia, Federica Barratta, Cesare Gregoretti, Giovanna Elisiana Carpagnano, Giovanni Misseri, SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia and Eisenmenger’s Syndrome: doubling the challenge , Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease: Early Access
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/monaldi.2022.2362
https://doi.org/10.4081/monaldi.2022.2362




